Powershell Environment Configuration: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "== Overview == Any issues and solutions that have been encountered configuring the Powershell environment to run scripts. == Script permissions == === Script permissions on...") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Any issues and solutions that have been encountered configuring the Powershell environment to run scripts. | Any issues and solutions that have been encountered configuring the Powershell environment to run scripts. | ||
== Creating and modifying environment variables == | |||
* [http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff730964.aspx Creating and Modifying Environment Variables] (Microsoft TechNet) | |||
=== Display all environment variables === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> Get-ChildItem Env: | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Display information about a particular environment variable === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> $Env:path | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Create a variable for the current session only === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> $env:TestVariable = "This is a test environment variable." | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== User- and machine-level environment variables === | |||
To create a persistent user-level environment variable: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("TestVariable", "Test value.", "User") | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* '''"TestVariable"''' is the name of the variable. | |||
* '''"Test Value."''' is the value assigned to the variable. | |||
* '''"User"''' is the level of the variable. `"User"` makes this a user-level variable. Alternate values are `"Machine"` and `"Process"`. | |||
Variables set with `SetEnvironmentVariable()` don't appear using the `Get-ChildItem env:` command until the current shell is closed and a new one is opened, although the value of the variable can be retrieved with | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("TestVariable","User") | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== Deleting environment varables === | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> Remove-Item Env:\TestVariable | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Or | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="powershell"> | |||
> [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("TestVariable", $null, "User") | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== Script permissions == | == Script permissions == | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 29 July 2014
Overview
Any issues and solutions that have been encountered configuring the Powershell environment to run scripts.
Creating and modifying environment variables
- Creating and Modifying Environment Variables (Microsoft TechNet)
Display all environment variables
> Get-ChildItem Env:
Display information about a particular environment variable
> $Env:path
Create a variable for the current session only
> $env:TestVariable = "This is a test environment variable."
User- and machine-level environment variables
To create a persistent user-level environment variable:
> [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("TestVariable", "Test value.", "User")
- "TestVariable" is the name of the variable.
- "Test Value." is the value assigned to the variable.
- "User" is the level of the variable.
"User"makes this a user-level variable. Alternate values are"Machine"and"Process".
Variables set with SetEnvironmentVariable() don't appear using the Get-ChildItem env: command until the current shell is closed and a new one is opened, although the value of the variable can be retrieved with
> [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("TestVariable","User")
Deleting environment varables
> Remove-Item Env:\TestVariable
Or
> [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("TestVariable", $null, "User")
Script permissions
Script permissions on the local filesystem
By default powershell scripts (.ps1) won't run. Permission for this doesn't allow for the local machine to execute powershell scripts.
[SCRIPT_NAME] : File [FULL_SCRIPT_PATH] cannot be loaded. The file [FULL_SCRIPT_PATH] is not digitally signed.
TODO: Document how to update the environment to allow this. I don't remember the details of how it was done right now.
Allowing scripts to run from UNC paths
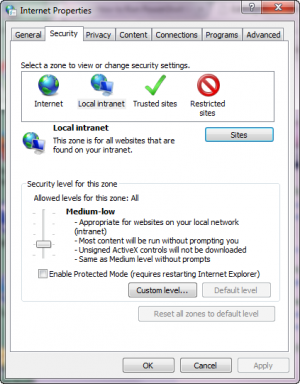
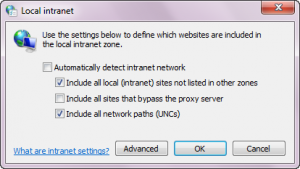
By default powershell scripts can't be run from UNC paths (e.g. \\mylocalserver\path\to\script.ps1):
[SCRIPT_NAME] : File [FULL_SCRIPT_PATH] cannot be loaded. The file [FULL_SCRIPT_PATH] is not digitally signed.
- Control Panel > Network and Internet > Internet Options > Security tab
- Select a zone to view or change security settings: Local Intranet
- Sites button
- Uncheck "Automatically detect intranet network"
- Check "Include all local (intranet) sites not listed in other zones"
- Check "Include all network paths (UNC)"
Aliases
There is a file that controls the current user's powershell environment. Scripts and script aliases are stored in this file.
TODO: I don't remember offhand where this file is located. Document its location.